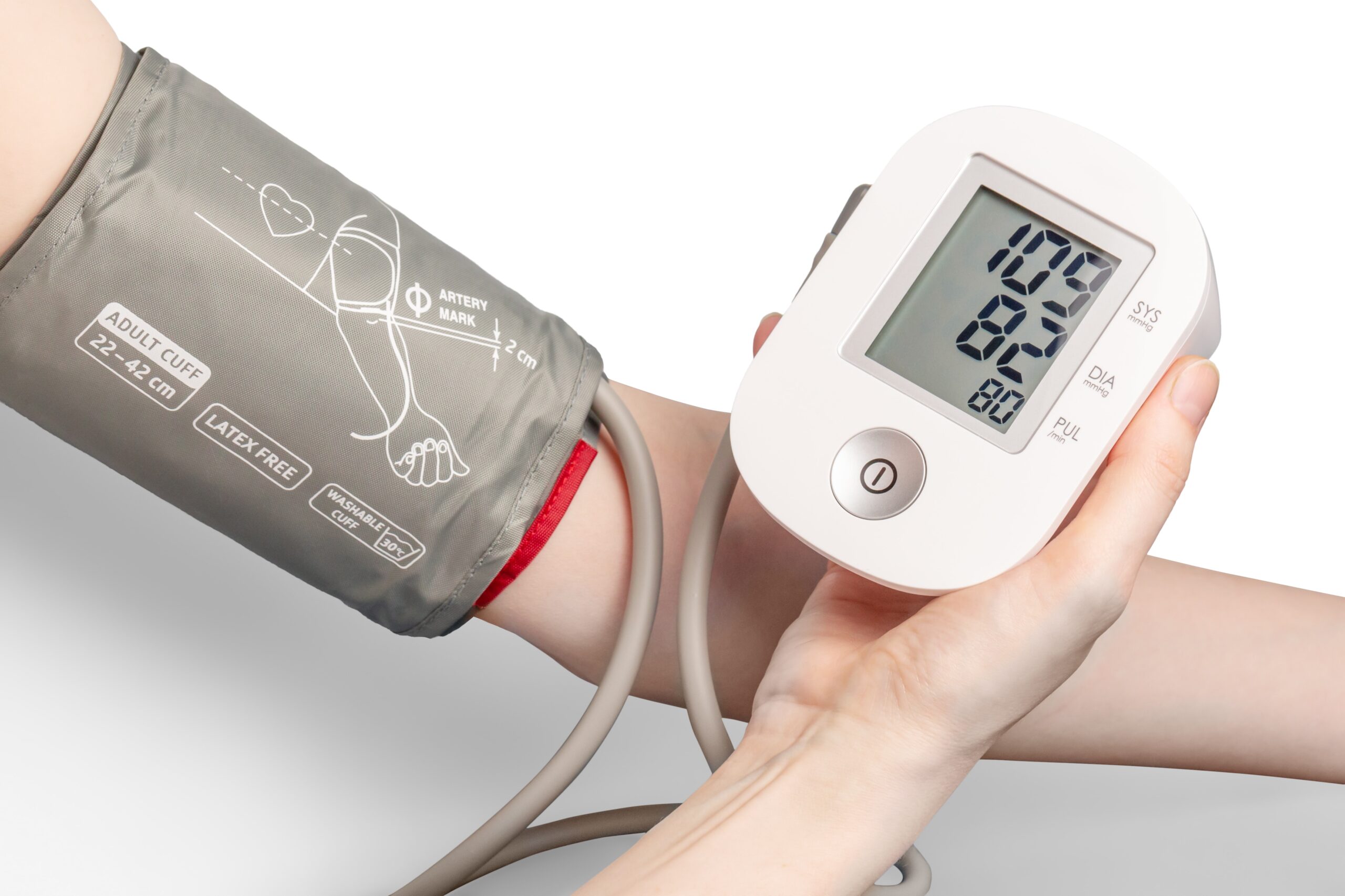
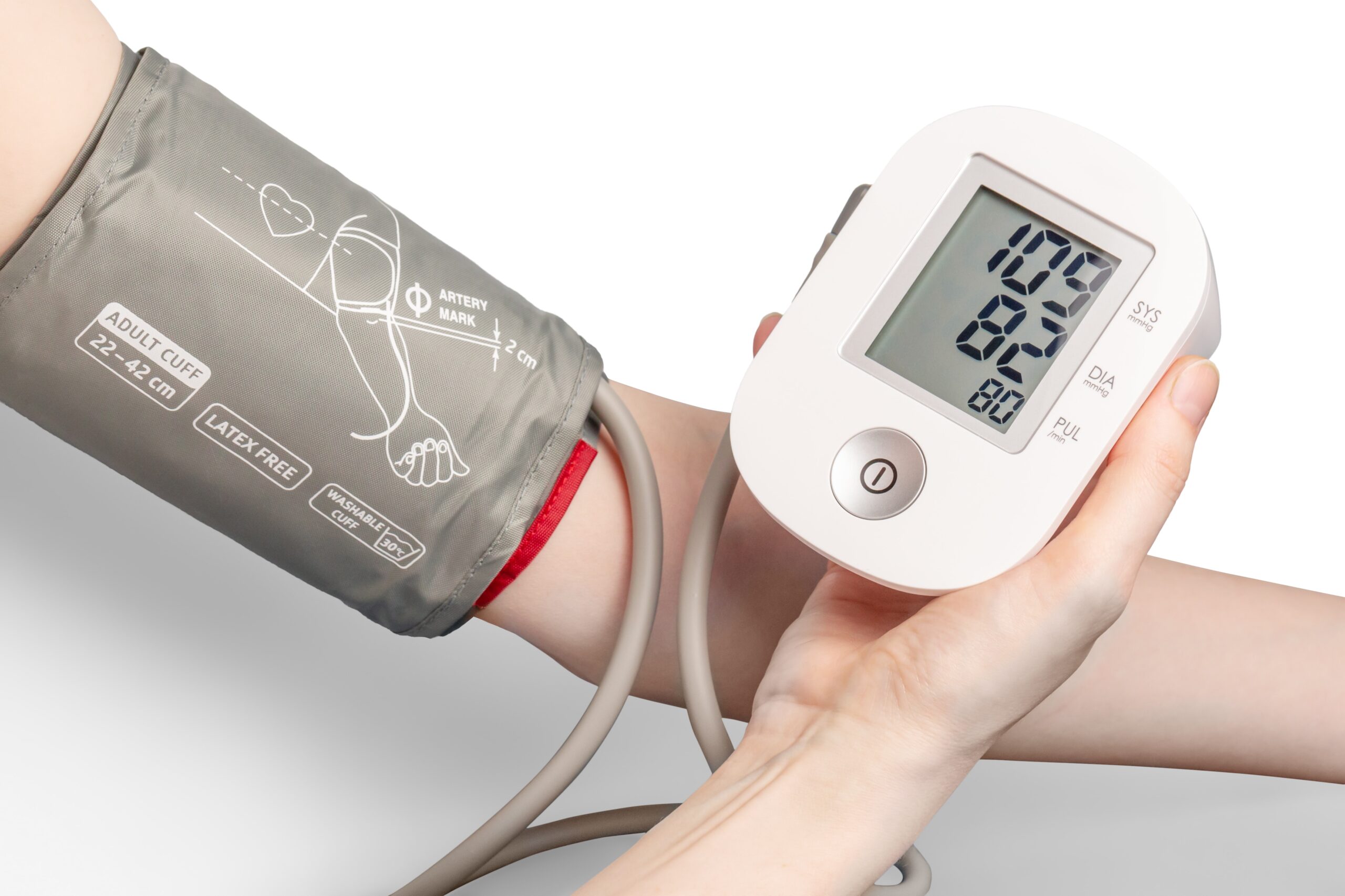
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is often referred to as a “silent killer” because it can go unnoticed for years without any obvious symptoms. However, it is important to be aware of the potential signs that may indicate high blood pressure, as it is a major risk factor for heart disease and other cardiovascular problems. In this article, we will explore the symptoms of high blood pressure and discuss recent scientific studies that have investigated this relationship.
Discover the Ultimate Weight Loss Secrets Here!
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a medical condition characterized by elevated blood pressure levels. It occurs when the force of blood against the walls of the arteries is consistently too high. This condition is prevalent globally and is a significant concern due to its potential impact on health. If left untreated, high blood pressure can lead to severe complications, including heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems.
Definition of high blood pressure
High blood pressure is defined as having systolic blood pressure (the top number) higher than 130 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure (the bottom number) higher than 80 mmHg. The measurements are typically recorded in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). A blood pressure of 120/80 mmHg is considered normal, while any reading above that range indicates the presence of high blood pressure.
Click Here for Proven Fat-Burning Strategies!
Prevalence and importance of high blood pressure
High blood pressure is a common condition that affects a significant portion of the population. According to recent studies, approximately one in three adults worldwide has hypertension. The prevalence increases with age, with older adults being at a higher risk. It is essential to address high blood pressure promptly as it is a leading cause of premature death and disability globally.
Risks associated with untreated high blood pressure
Untreated high blood pressure can have severe consequences on your health. It can lead to various complications, such as heart attack, heart failure, stroke, aneurysm, kidney problems, and peripheral arterial disease. Moreover, it can potentially damage vital organs like the heart, brain, kidneys, and eyes. Pregnant individuals with untreated high blood pressure are also at risk of pregnancy complications, including preeclampsia.
Primary Symptoms
High blood pressure often presents with several primary symptoms. While these symptoms may not always be present, they serve as markers for potential hypertension.
Headache
One of the primary symptoms of high blood pressure is a persistent headache, often described as a dull or throbbing pain. This headache may be particularly prominent in the morning or after physical exertion.
Dizziness and lightheadedness
Feeling dizzy or lightheaded can be a symptom of high blood pressure. This sensation may be more noticeable when rising from a sitting or lying position, and it can occur due to inadequate blood flow to the brain.
Blurred or double vision
High blood pressure can affect vision by causing blurred or double vision. This symptom is usually temporary and resolves once blood pressure levels are normalized.
Nosebleeds
Frequent nosebleeds or sudden episodes of bleeding from the nose can be indicative of high blood pressure. It is important to note that nosebleeds can also be caused by other factors, so they should not be solely relied upon for diagnosis.
Shortness of breath
In some cases, high blood pressure can result in shortness of breath, especially during physical activities or exertion. This symptom may occur due to reduced blood flow to the lungs or fluid accumulation in the lungs.
Chest pain
Chest pain or discomfort can be associated with high blood pressure, particularly in individuals with pre-existing heart conditions. Chest pain may indicate angina, a condition caused by reduced blood flow to the heart.
Irregular heartbeat
An irregular heartbeat, also known as arrhythmia, can be a symptom of high blood pressure. It can manifest as a racing heart, palpitations, or a sensation of skipped beats. If you experience an irregular heartbeat, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
Secondary Symptoms
In addition to the primary symptoms, high blood pressure can also lead to various secondary symptoms. These symptoms may not be directly caused by high blood pressure but can occur as a consequence of the condition.
Fatigue
Feeling tired or fatigue is a common secondary symptom of high blood pressure. The condition can affect overall energy levels and lead to a constant feeling of exhaustion.
Confusion
High blood pressure can impair cognitive function and cause confusion or difficulty in concentrating. Individuals may experience memory problems, trouble finding words, or confusion in everyday tasks.
Tinnitus
Tinnitus, or a ringing sensation in the ears, has been associated with high blood pressure. This symptom can be bothersome and interfere with daily activities.
Anxiety
High blood pressure can contribute to feelings of anxiety or heightened stress levels. Managing stress and anxiety is crucial in controlling blood pressure and overall well-being.
Nausea
Some individuals with high blood pressure may experience nausea or an uneasy feeling in the stomach. This symptom can be triggered by the effects of elevated blood pressure on the digestive system.
Blood in urine
The presence of blood in urine, also known as hematuria, may be an indication of high blood pressure. It is important to seek medical attention if you notice this symptom, as it can have various underlying causes.
Pounding in chest, neck, or ears
A sensation of pounding or throbbing in the chest, neck, or ears can occur with high blood pressure. This symptom is often described as a heightened awareness of the heartbeat.
Difficulty sleeping
High blood pressure can impact sleep patterns and lead to difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep. Sleep disturbances can contribute to fatigue and overall discomfort.
Swelling in the ankles, feet, legs, or abdomen
Swelling, also known as edema, can occur in individuals with high blood pressure. It usually affects the ankles, feet, legs, or abdomen and may be a result of fluid retention.
Heavy sweating
Excessive sweating, particularly when not associated with physical activity or high temperatures, can be a secondary symptom of high blood pressure. It is often experienced as profuse or unstinting perspiration.

Silent Symptoms
In some cases, high blood pressure may present with no visible symptoms at all. This is why it is often referred to as the “silent killer.” Despite the absence of apparent symptoms, untreated high blood pressure can silently cause significant damage to organs and overall health.
No symptoms at all
It is crucial to note that high blood pressure can exist without any noticeable symptoms. Regular blood pressure checks are essential to detect hypertension early and prevent its associated complications.
Damage to organs
Silently and without evident symptoms, high blood pressure can wreak havoc on vital organs such as the heart, brain, kidneys, and eyes. Over time, elevated blood pressure can cause significant damage to these organs, leading to potentially life-threatening conditions.
Potential effects on pregnancy
Pregnant individuals may experience high blood pressure during pregnancy, a condition known as gestational hypertension. If left untreated, gestational hypertension can complicate the pregnancy and pose risks to the health of both the mother and the baby. Regular prenatal check-ups are critical in monitoring blood pressure levels during pregnancy.
Individual Variations
Symptoms of high blood pressure can vary from person to person, depending on several factors, including individual differences, gender, age, and race/ethnicity.
Variability in symptoms
It is important to recognize that the symptoms of high blood pressure can vary significantly among individuals. While some individuals may experience noticeable primary symptoms, others may only present with secondary symptoms or no symptoms at all. Regular blood pressure checks are necessary for accurate diagnosis.
Gender differences
Research suggests that symptoms of high blood pressure may differ between genders. While men may experience symptoms such as chest pain and irregular heartbeat more commonly, women may experience symptoms like fatigue, confusion, and shortness of breath.
Influence of age
The prevalence of high blood pressure increases with age, and symptoms may vary accordingly. Older individuals may be more likely to experience symptoms such as headache, dizziness, and shortness of breath.
Influence of race/ethnicity
Research has shown that certain racial and ethnic groups may have a higher prevalence of high blood pressure and its associated symptoms. African Americans, for example, tend to develop high blood pressure earlier in life and are more likely to experience symptoms such as chest pain and shortness of breath.
Diagnosis
Early detection of high blood pressure is crucial for effective management. Diagnosis typically involves regular blood pressure check-ups and monitoring techniques.
Regular blood pressure check-ups
Regular blood pressure check-ups are essential in identifying and diagnosing high blood pressure. Healthcare professionals use blood pressure monitors, usually a cuff placed around the arm, to measure and record blood pressure levels.
Home-based blood pressure monitoring
Home-based blood pressure monitors allow individuals to measure their blood pressure regularly in the comfort of their own homes. This method can provide a more comprehensive picture of blood pressure trends over time and help in early detection.
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring
For individuals with suspected white-coat hypertension or those who require more accurate blood pressure readings, ambulatory blood pressure monitoring may be used. This involves wearing a portable blood pressure monitor for 24 hours, which takes frequent readings throughout the day and night.
White-coat hypertension
White-coat hypertension refers to temporarily elevated blood pressure levels that occur solely in a clinical setting due to anxiety or stress. It is important to differentiate white-coat hypertension from persistent high blood pressure to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Complications
Untreated high blood pressure can lead to various complications that significantly impact overall health and well-being. It is essential to manage and control blood pressure effectively to prevent these complications.
Heart attack
High blood pressure increases the risk of heart attack by putting excessive pressure on the heart and blood vessels. Over time, this strain can weaken the heart and lead to a heart attack, a potentially life-threatening condition.
Heart failure
Persistent high blood pressure can cause the heart to work harder, eventually leading to heart failure. Heart failure occurs when the heart is unable to pump blood effectively, leading to fluid buildup in the lungs and other parts of the body.
Stroke
A stroke, often caused by a burst or blocked blood vessel in the brain, is a serious complication of high blood pressure. The increased pressure can weaken blood vessels over time, making them more susceptible to rupturing.
Aneurysm
High blood pressure can contribute to the formation and rupture of an aneurysm, a weakened and bulging blood vessel. An aneurysm rupture can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
Kidney problems
Chronic high blood pressure can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to kidney disease or even kidney failure. Individuals with high blood pressure should regularly monitor their kidney function to prevent long-term complications.
Peripheral arterial disease
High blood pressure can negatively impact blood circulation through the narrowing of blood vessels. This can result in peripheral arterial disease, characterized by reduced blood flow to the limbs, leading to pain, impaired wound healing, and increased risk of infection.

Risk Factors
Several risk factors contribute to the development of high blood pressure. Understanding these factors can help in the prevention and management of hypertension.
Family history
Having a family history of high blood pressure can increase your risk of developing the condition. If your parents or close relatives have hypertension, it is important to be vigilant and regularly monitor your blood pressure.
Age
As mentioned earlier, the prevalence of high blood pressure increases with age. The risk of developing hypertension rises significantly after the age of 40 and continues to increase as individuals grow older.
Race/ethnicity
Certain races and ethnicities have a higher prevalence of high blood pressure. African Americans, for instance, tend to have higher rates of hypertension, while individuals of Asian descent may have a higher risk of developing high blood pressure at lower blood pressure levels.
Gender
Men and women may have different risks and symptoms associated with high blood pressure. Men are generally at a higher risk of developing hypertension at a younger age, while women may be at an increased risk post-menopause.
Tobacco use
Smoking and tobacco use significantly increase the risk of high blood pressure. The chemicals in tobacco can damage blood vessels and make them more susceptible to the effects of elevated blood pressure.
Poor diet
A diet high in sodium, saturated fats, and cholesterol can contribute to high blood pressure. Additionally, a lack of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in the diet can deprive the body of essential nutrients needed to maintain healthy blood pressure levels.
Lack of physical activity
A sedentary lifestyle and lack of regular exercise can increase the risk of high blood pressure. Engaging in physical activity helps strengthen the heart and blood vessels, leading to better blood pressure control.
Obesity
Being overweight or obese is a significant risk factor for high blood pressure. Excess weight puts additional strain on the heart and blood vessels, leading to elevated blood pressure levels.
Excessive alcohol consumption
Heavy alcohol consumption can contribute to high blood pressure. Excessive drinking can damage the heart and blood vessels, leading to hypertension and other cardiovascular complications.
Stress
Chronic stress and elevated levels of stress hormones can contribute to high blood pressure. Effective stress management techniques, such as exercise, meditation, and relaxation techniques, are crucial in controlling blood pressure.
Chronic conditions
Certain chronic conditions such as diabetes, kidney disease, and sleep apnea can increase the risk of high blood pressure. It is important to manage these conditions effectively to prevent the development or worsening of hypertension.
Healthy Lifestyle Modifications
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is vital in managing and controlling high blood pressure. Adopting the following modifications can have a positive impact on blood pressure levels.
Dietary changes
A balanced diet low in sodium and rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help in managing blood pressure. The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet is a recommended dietary approach for individuals with hypertension.
Regular exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity can help control blood pressure. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise.
Weight loss
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can have a significant impact on blood pressure. Losing even a small amount of excess weight can lead to improvements in blood pressure levels.
Stress management
Effective stress management techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and hobbies can help reduce stress and, consequently, blood pressure levels.
Smoking cessation
Quitting smoking is crucial in preventing and managing high blood pressure. Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of heart disease and other complications associated with hypertension.
Limiting alcohol intake
Moderate alcohol consumption is defined as up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men. Excessive alcohol consumption can increase blood pressure, so it is important to drink in moderation.
Conclusion
High blood pressure is a prevalent condition with significant implications on overall health. It is essential to seek medical advice and regularly monitor blood pressure levels to detect hypertension early. Managing and controlling high blood pressure through lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular check-ups is crucial in preventing complications and maintaining a good quality of life. Remember, early detection and intervention can play a pivotal role in reducing the risks associated with high blood pressure and protecting your long-term health.